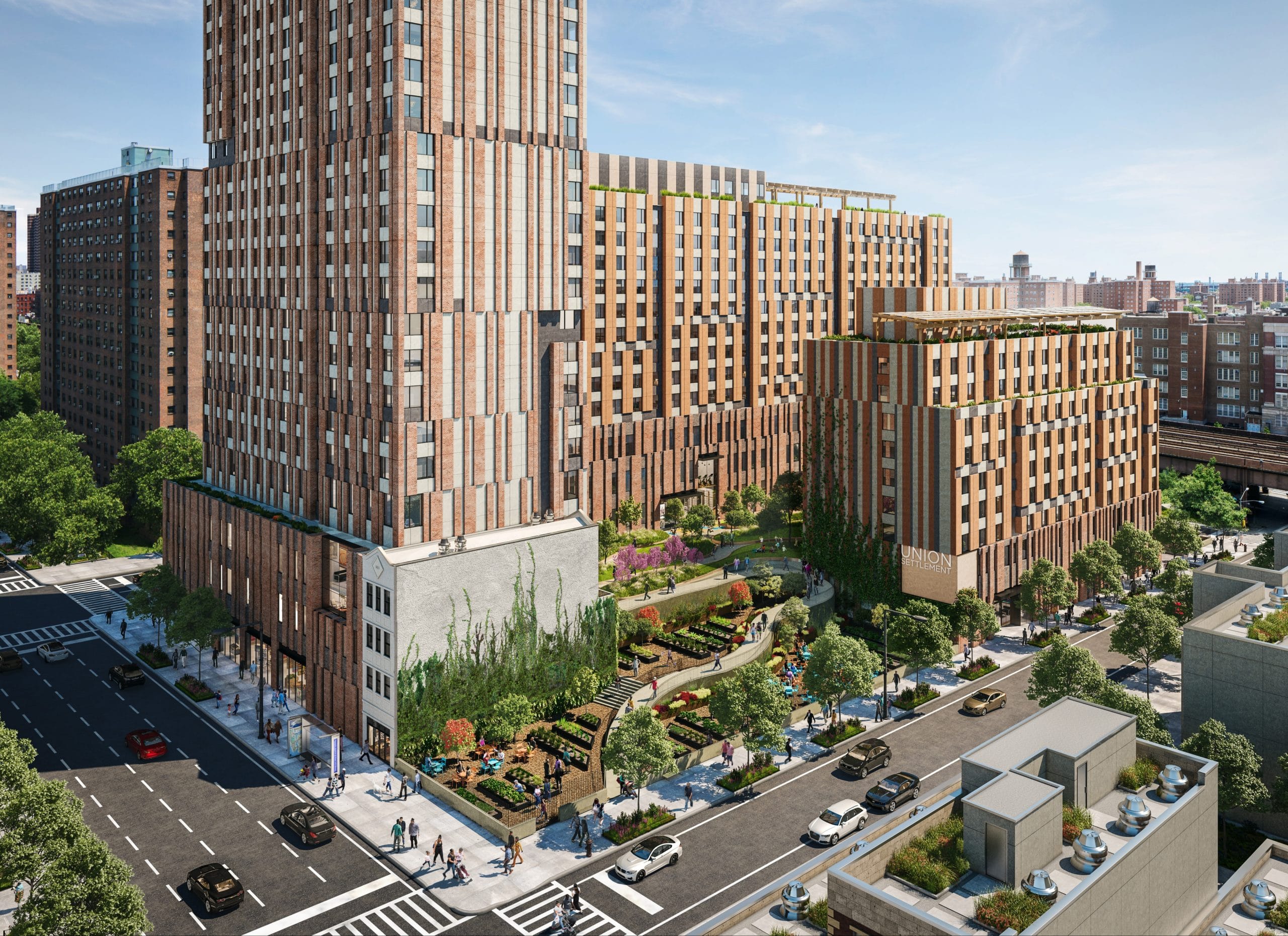
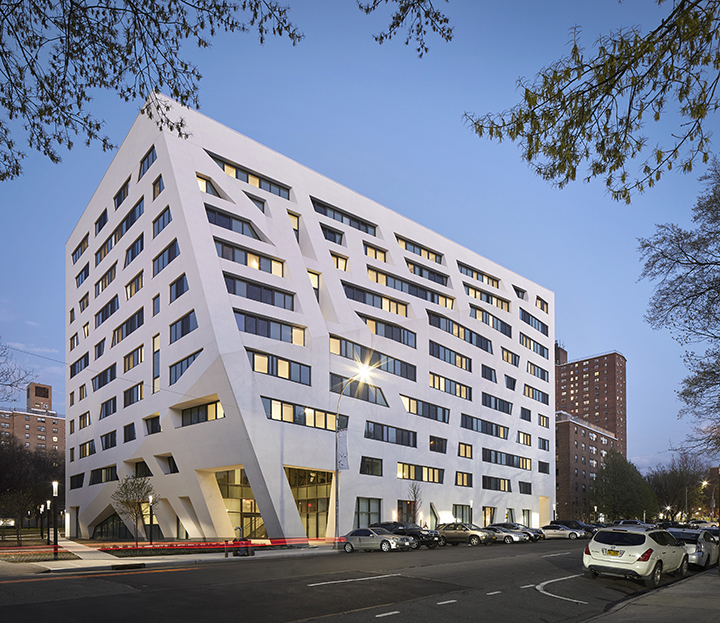
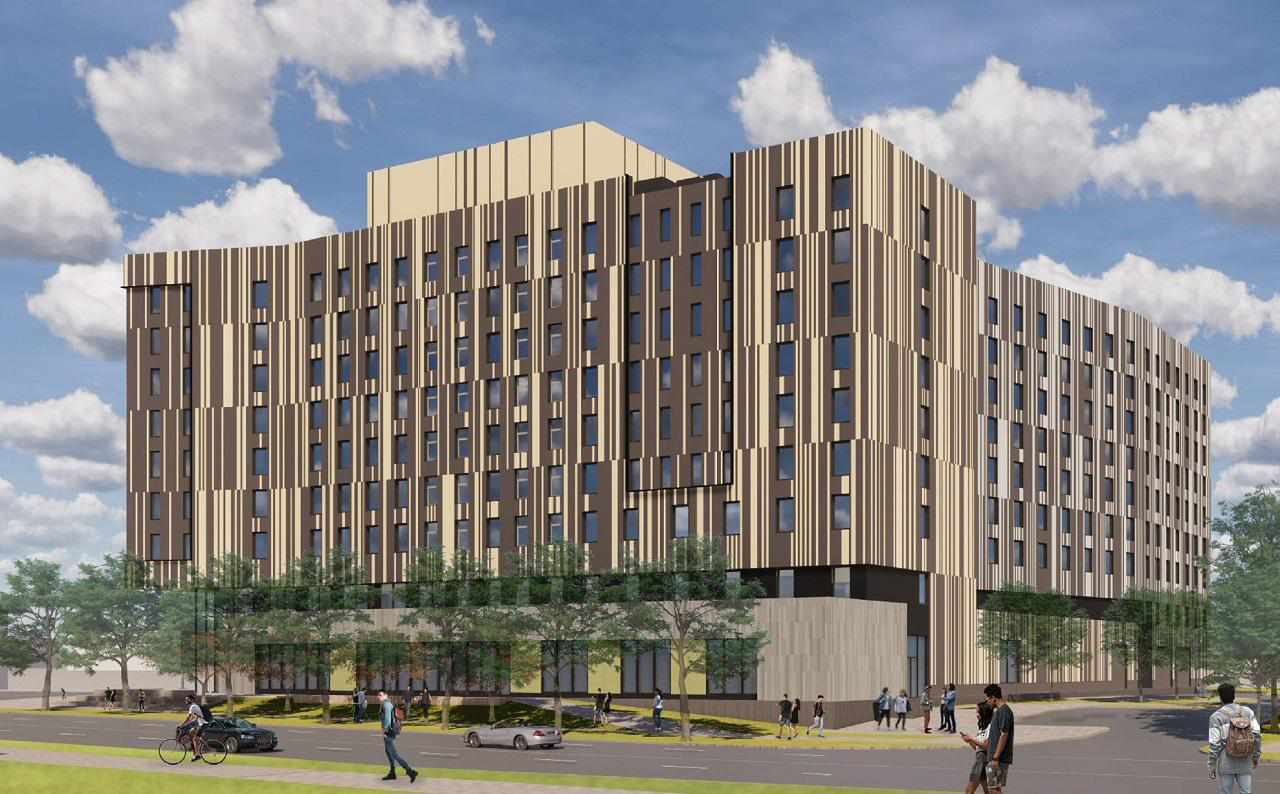
Start an Evolution.
We help you identify progressive solutions to improve the built environment.
Leaders in energy, sustainability, and
accessibility consulting since 1972.

Click hot spots to see our work-in-action.
We Make Buildings Perform Better
For over five decades, we’ve been at the forefront of transforming the built environment to be more energy efficient, accessible, healthy, and resilient.
Sustainable Design & Construction
Our consulting services are designed to help you achieve your climate, compliance, equity, and financial objectives. We help you create low-energy buildings that perform well today and provide long-term resiliency.
Energy Efficiency & Decarbonization
Around 80% of the buildings that will exist in 2050 are already built. Our team helps clients to analyze and improve the systems and operations of these buildings so they can meet the performance requirements and mitigate climate impact.
Accessibility
Our team ensures that every project meets all code and regulatory requirements for accessible design and construction—now and for the lifespan of a building—preventing costly retrofits that can result from potential litigation.
What We’re Working On
Industry Leading Insights
Who We Work With
We collaborate with developers, owners, managers, agencies, architects, and many others. Below are a few examples of our clients.