As seen in:
Humans have been trying to harness the power of the sun for millennia. The advent and popularization of photovoltaics in the latter half of the twentieth century made doing so accessible to the masses. Today, solar arrays are commonly seen adorning the roofs of suburban homes and “big-box” retailers, as well as on other landscapes including expansive solar farms and capped landfills. Until recently, the common thread amongst these locations has been the employment of open space. Solar applications have historically been reserved for use in areas of low-to-moderate building density.
By the end of 2050, solar energy is projected to be the world’s largest source of electricity. While utility-scale solar will comprise the majority of this capacity, there will also be significant growth in the commercial and residential sectors – particularly in cities. Industry influencers are increasingly focused on creating opportunities for solar applications in high-density areas, where much of the demand lies.
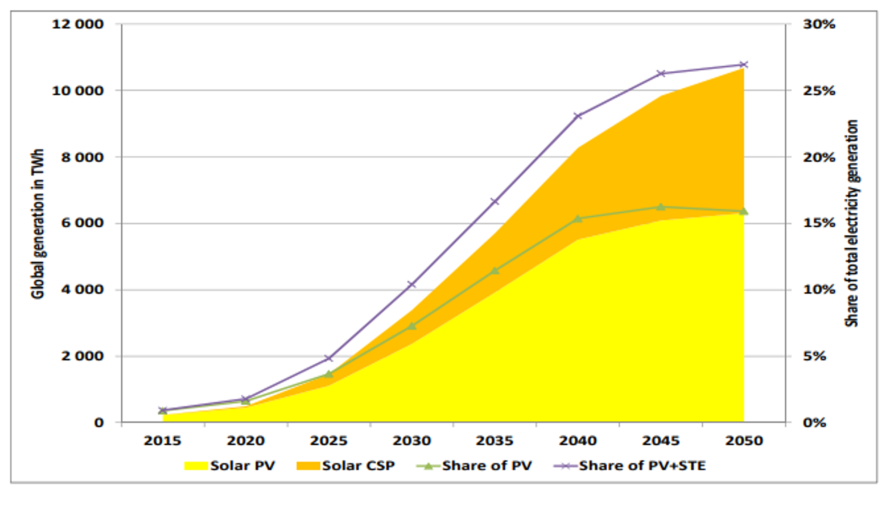 In their 2014 Technological Roadmaps for solar PV and solar thermal electricity (STE), the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts Solar PV and STE to represent over 25% of global electricity generation by 2050.
In their 2014 Technological Roadmaps for solar PV and solar thermal electricity (STE), the International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts Solar PV and STE to represent over 25% of global electricity generation by 2050.

