If you recall from Part 1 of this article written back in September, we discussed why exhaust fans often don’t operate as they are intended. Now, let’s discuss how to rectify these issues. First, we need to understand that all fans are not created equal. To do this, SWA participated in a “blind” study that analyzed a number of today’s common exhaust fans. The study emphasizes the importance of fan selection. With this understanding, we will then discuss solutions and best practices for installing bathroom exhaust ventilation.
The “Blind” Study
To get a comprehensive performance dataset for a number of exhaust fans, the Riverside Energy Efficiency Laboratory (REEL) was engaged for a “blind” study. REEL is the HVI/ESTAR neutral, third-party testing facility. In total, 7 multi-speed fans, 7 single speed fans, and 6 low-profile fans from six manufacturers were sent to REEL without manufacturer markings. In general, ten-point airflow tests were conducted on each fan. Testing adhered to standards used in the industry, namely, ANSI/AMCA Standard 210 and HVI Publications 916 and 920, where applicable. While the dataset is extensive, this paper focuses on the 50, 80, and 110 cfm ventilation rates, as these are the most common specified fan speeds for bathrooms. These fan curves show the relationship of airflow that will be delivered at various static pressures of the duct system.
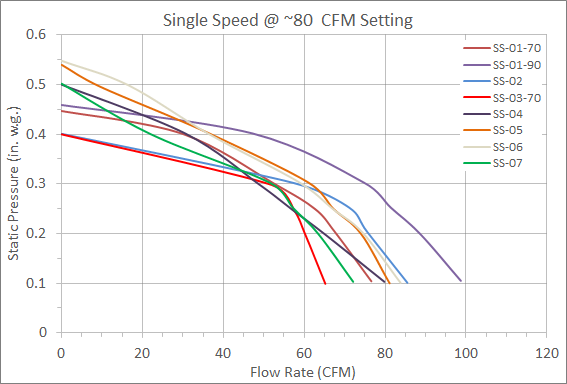
Figure 1 shows fan curves for single speed fans that were tested. The units are rated for 80 cfm unless noted otherwise in the legend (two are rated for 70 cfm and one for 90 cfm). While all of these fans performed in a similar manner, would it surprise you that two of the fan curves in Figure 1 are for exhaust fans that use DC motors? People often assume that all fans using DC motors are the same and result in constant airflow for a range of static pressures (let’s say up to 0.4” w.g.).
It is clear in this data (Figure 1) that flow rates decrease rapidly when static pressure rises over 0.3” w.g., as it often does in real world installations. Oh, are you still wondering which two fans have DC motors? It is actually SS-05 and SS-06. A bit surprising, isn’t it?